Inflammation & Hyperbaric Therapy
- Share
- Issue Time
- Aug 12,2024
Summary
Inflammation & hyperbaric therapy


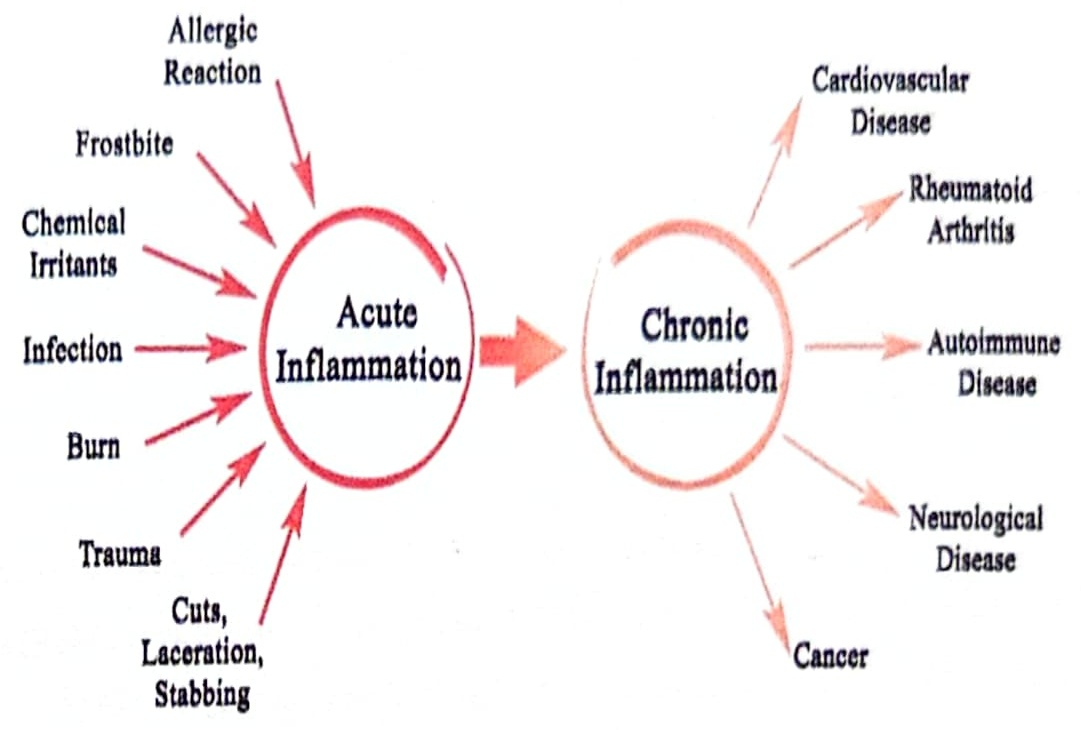
Inflammation is part of the body's natural defense mechanism. While it plays an important role in the healing process, it is often the cause of painful and challenging symptoms as well as tissue damage that can be caused by diseases and injuries.
When tissues experience trauma,the body's natural inflammatory process is usually triggered. While helpful at the onset,the lasting impacts can result in many unwanted effects.
The inflammatory process is designed to be the body's damage control system, and is responsible for responding quickly to any kind of injury.
Unfortunately,collateral damage to healthy tissue can occur from the process. The physi-cal results of the inaflammatory process can be uncomfortable, especially in cases where it becomes chronic.
How Hyperbarics Can Help
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy has been proven to positively influence 8,101 genes.
Particularly significant are the genes responsi-ble for decreasing inflammation and triggering tissue repair.
Research shows that hyperbaric therapy may:
Reduce inflammation
Stimulate tissue healing and re-pair
Reduce pain and swelling
Shorten recovery time after injury or surgical procedures
Positively affect 40% of human genome
Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen
Therapy on Inflammation,
Oxidative/Antioxidant Balance,and
Muscle Damage after Acute Exercise
in Normobaric,Normoxic and
Hypobaric,Hypoxic Environments:
A Pilot Study
Jinhee Woo.Jae-Hee Min,Yul-Hyo Lee and Hee-Tae
Roh Published: 10 October 2020
Abstract: The purpose of this study was to
investigate the effects of hyperbaric oxygen
therapy (HBOT) on inflammation,the
oxidative/antioxidant balance, and muscle
damage after acute exercise in normobaric,
normoxic (NN) and hypobaric,hypoxic (HH)
environments...
Results suggest that acute exercise in both the NN and HH environments could induce temporary inflammatory responses and muscle damage,whereas HBOT treatment may be effective in alleviating exercise-induced inflammatory responses and muscle damage.